MACD Analysis in Forex: A Complete Trading Guide
[ad_1] Are you having trouble making money in Forex trading? The currency markets can be very unpredictable. But, there’s a tool that can help you. It’s called the MACD indicator. This guide will teach you how to use it to improve your trading. The MACD indicator is special because it looks at trends and momentum
[ad_1]

Are you having trouble making money in Forex trading? The currency markets can be very unpredictable. But, there’s a tool that can help you. It’s called the MACD indicator. This guide will teach you how to use it to improve your trading.
The MACD indicator is special because it looks at trends and momentum together. Learning to use MACD can give you an advantage. You’ll be able to spot market changes and make better choices. Are you ready to get better at Forex trading? Let’s explore the MACD together.
Key Takeaways
- MACD combines trend and momentum analysis.
- Standard settings: 12 (fast EMA), 26 (slow EMA), 9 (signal line).
- Crossovers and zero-line crosses indicate possible trade signals.
- The histogram height shows how strong the momentum is.
- Divergences can signal trend reversals.
- Using MACD with other indicators makes it more accurate.
Understanding the Fundamentals of MACD
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) is a key tool in forex trading. It helps traders spot market trends and when to buy or sell. Let’s dive into what makes up this indicator and its history.
What is MACD and Its Core Components
MACD has three main parts that give trading signals:
- MACD Line: The difference between 12-period and 26-period Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs)
- Signal Line: A 9-day EMA of the MACD Line
- Histogram: The visual representation of the distance between MACD and Signal lines
The MACD Formula Explained
The MACD formula is simple yet powerful:
MACD = 12-period EMA – 26-period EMA
This formula creates the MACD line. The signal line is a 9-day EMA of the MACD line.
Historical Development and Significance
Gerald Appel created the MACD in the 1970s. It’s now a key part of technical analysis. Traders love it for showing trend direction, strength, and reversals.
The MACD works well for both short and long-term trading. It’s a favorite in the forex market.
| MACD Component | Description | Typical Settings |
|---|---|---|
| MACD Line | Difference between fast and slow EMAs | 12-26 periods |
| Signal Line | EMA of MACD Line | 9 periods |
| Histogram | MACD Line – Signal Line | N/A |
MACD Analysis in Forex
MACD Forex strategies are key in analyzing currency pairs. This tool helps spot trends and possible reversals in the fast Forex market. The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator has two lines and a histogram. It gives traders valuable insights for making trading decisions.
In Forex trading, MACD is used on charts like 30-minute, 1-hour, 4-hour, and daily ones. The usual settings are 12 and 26-period exponential moving averages (EMAs) with a 9-period signal line. These settings can be changed to fit different trading styles and market conditions.
MACD Forex strategies rely on several key signals:
- Bullish crossover: MACD line crosses above the signal line
- Bearish crossover: MACD line crosses below the signal line
- Zero line crossovers: Indicate shifts in market sentiment
- Histogram analysis: Measures momentum and possible trend reversals
Using MACD for currency pair analysis works best in trending markets with narrow price ranges. Traders often use MACD with other indicators like RSI or Bollinger Bands for better signals. While MACD is great at finding trends, it’s important to remember that signals might lag behind price action. This requires careful interpretation and risk management.
Essential Components of the MACD Indicator
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator has three main parts. They help traders spot trend changes and market momentum. These parts are key for forex trading insights.
MACD Line and Signal Line
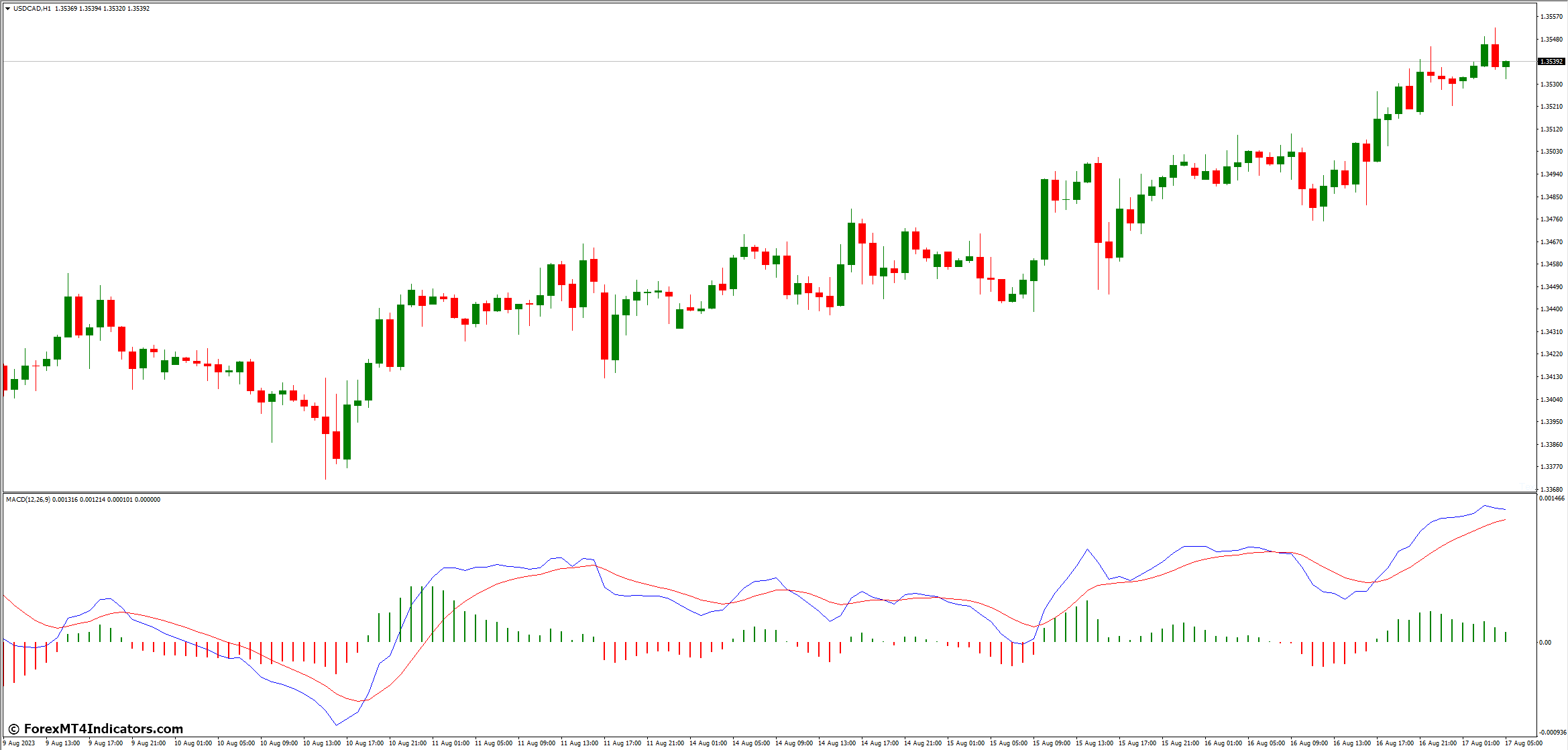

The MACD line is central to this indicator. It’s made by subtracting a 26-period EMA from a 12-period EMA. The signal line, a 9-period EMA of the MACD line, triggers buy and sell signals. When these lines cross over, it signals a trend shift.
MACD Histogram
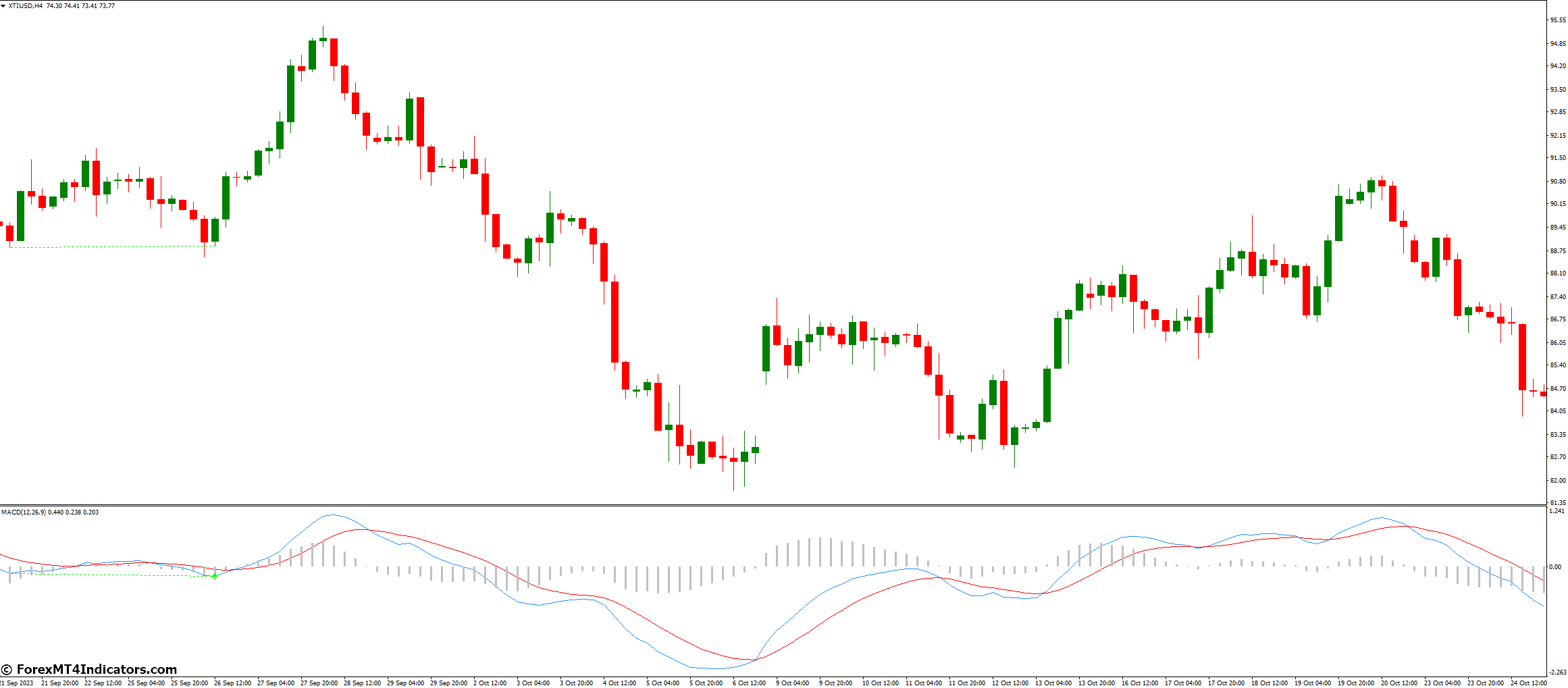

The histogram shows the difference between the MACD and signal lines. It helps traders see momentum strength. Longer bars mean stronger momentum, while shorter bars show weakening momentum. This analysis is key for spotting trend reversals or continuations.
Zero Line Reference
The zero line is a key reference in MACD analysis. When the MACD goes above the zero line, it’s bullish. Going below is bearish. This helps traders understand the market sentiment in forex.
| Component | Calculation | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| MACD Line | 12-period EMA – 26-period EMA | Measures short-term momentum |
| Signal Line | 9-period EMA of MACD Line | Generates buy/sell signals |
| Histogram | MACD Line – Signal Line | Visualizes momentum strength |
Knowing these parts helps traders make smart forex decisions. By looking at MACD crossovers, analyzing histograms, and checking the zero line, traders can find good entry and exit points.
Reading MACD Signals for Forex Trading

MACD signals are key in forex trading. They help traders find the best times to buy or sell. Knowing how to read these signals can help with trading choices.
Bullish and Bearish Crossovers
MACD crossovers show market direction. A bullish signal happens when the MACD line goes above the signal line. This means the market might go up. On the other hand, a bearish signal shows when the MACD line goes below the signal line. This means the market might go down.
| Signal Type | MACD Line Position | Market Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish | Above Signal Line | Potential Uptrend |
| Bearish | Below Signal Line | Potential Downtrend |
Zero Line Crossovers
Zero-line crossovers help confirm trend direction. A MACD line crossing above the zero line means a bullish trend. Crossing below the zero line means a bearish trend.
Histogram Analysis Techniques
The MACD histogram shows price momentum. Longer bars mean more momentum, while shorter bars mean less. Traders use these patterns to spot trend changes in forex pairs.
Using these MACD analysis methods can help traders make better choices. Remember, MACD signals are powerful but should be used with other indicators for the best results.
MACD Trading Strategies for Forex Markets
The MACD trading system offers many Forex MACD strategies for traders. Gerald Appel created it in the late 1970s. It’s now a key tool in technical analysis. Let’s look at some effective MACD-based strategies for Forex.
The histogram strategy looks at the MACD histogram’s height changes. Bars moving away from zero signal a market reversal. Bars near zero mean the market will keep going.
The crossover strategy is also popular. It gives buy signals when the MACD line goes above the signal line. Sell signals happen when it goes below. This method helps spot trend changes in currency pairs.
The zero-cross strategy is simple yet effective. An uptrend starts when the MACD line goes above zero. A downtrend starts when it goes below. This strategy confirms the market’s direction.
| Strategy | Buy Signal | Sell Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Histogram | Bars moving away from zero (upward) | Bars moving away from zero (downward) |
| Crossover | MACD line crosses above the signal line | MACD line crosses below the signal line |
| Zero-Cross | MACD line crosses above the zero line | MACD line crosses below the zero line |
Advanced traders use MACD with other indicators like the Money Flow Index (MFI). A bearish trend confirmed by both MACD and MFI means the market is overbought. A bullish trend means it’s oversold.
Remember, tweaking MACD settings for specific currency pairs and timeframes can boost trading results. Try out these Forex MACD strategies to find what works best for you.
MACD Divergence Patterns and Their Significance
MACD divergence is key in forex trading. It warns of trend changes or continuations. About 70% of traders use it for early signals.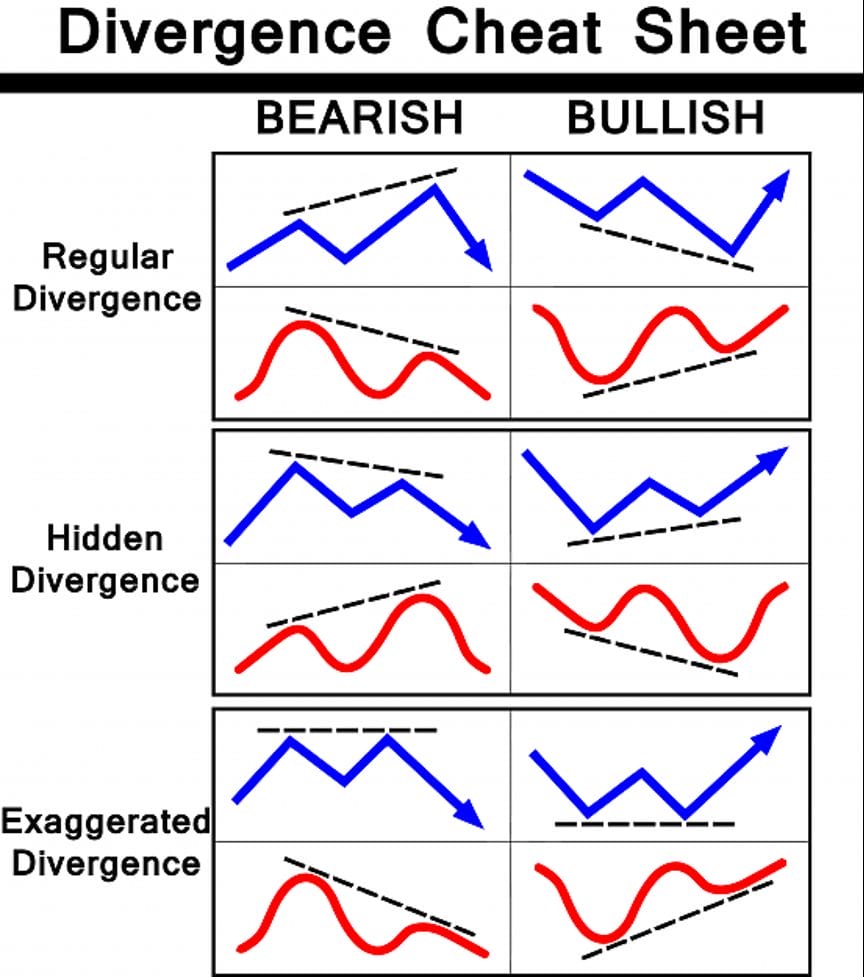

Regular Divergence Patterns
Regular divergence often signals a trend change. It happens in 60% of cases when price and MACD don’t match. Bullish divergence shows when prices drop but MACD rises. Bearish divergence is when prices rise but MACD falls.
Hidden Divergence Patterns
Hidden divergence points to trend continuation, making up 40% of patterns. It’s less common but vital. Hidden bullish divergence shows price highs but MACD lows. Hidden bearish divergence shows price lows but MACD highs.
Trading Divergence Successfully
To trade MACD divergence well, use it with other tools. Over 55% of traders use MACD for spotting divergence. Pairing it with RSI boosts signal accuracy by 25%. Use stop-loss orders, used by 80% of successful traders.
| Divergence Type | Price Action | MACD Action | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Bullish | Lower Lows | Higher Lows | Potential Uptrend |
| Regular Bearish | Higher Highs | Lower Highs | Potential Downtrend |
| Hidden Bullish | Higher Lows | Lower Lows | Trend Continuation |
| Hidden Bearish | Lower Highs | Higher Highs | Trend Continuation |
Multiple Timeframe Analysis with MACD
MACD timeframes are key in forex trading. They help traders see market trends. This method, called multi-timeframe analysis, links short-term trades with long-term trends.
Traders mix different timeframes to make smart choices. They might use daily charts for big trends, 4-hour charts for timing, and 1-hour charts for exact entry points. This way, they can trade more consistently and solve signal conflicts.
Trading experts say timeframes in a cycle usually range from 4 to 6. Dr. Elder recommends a factor of five between each time frame. For example, if daily data is in the middle, the shorter interval is 1-2 hours, and the longer is one week.
Here’s a list of common timeframes in forex trading:
- Short-term: 1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute bars
- Medium-term: 30-minute, 1-hour, 4-hour bars
- Long-term: Daily, weekly, monthly bars
Day traders look at short timeframes for quick profits. Position traders use longer timeframes for long-term trends. By using MACD from various timeframes, traders can boost their success and get better risk-to-reward ratios.
Combining MACD with Other Technical Indicators
Traders mix MACD with other tools for better forex analysis. This mix helps make trading choices more accurate. It gives a full view of the market.
MACD with RSI
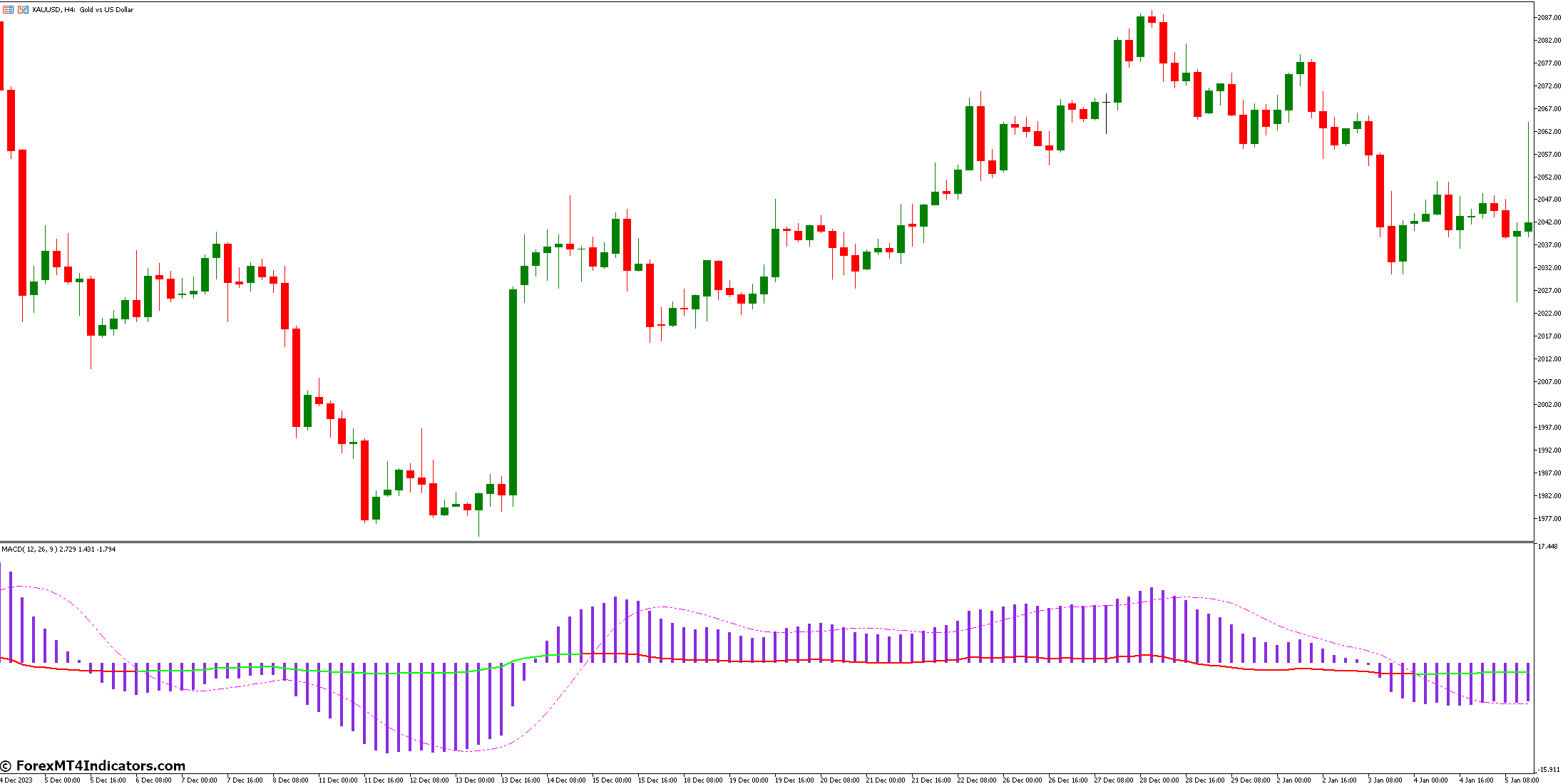

The MACD RSI combo is a strong tool for forex traders. MACD shows trend direction and momentum. RSI checks if prices are too high or too low. When they match, it points to good trade chances.
MACD with Moving Averages
Using MACD with moving averages adds to trend confirmation. The 12 and 26-day EMAs in MACD work well with longer averages. They help spot big market trends.
MACD with Volume Analysis
Adding volume analysis to MACD checks price moves. High volume with MACD crossovers shows strong trend changes. Low volume might mean weak signals.
| Indicator Combination | Benefits | Application |
|---|---|---|
| MACD + RSI | Confirms momentum and overbought/oversold conditions | Entry/exit point refinement |
| MACD + Moving Averages | Enhances trend identification | Long-term trend trading |
| MACD + Volume | Validates price movements | Trend strength assessment |
By mixing these indicators, traders can build stronger strategies. It’s key to avoid too much repetition. Each tool should offer something unique.
Common MACD Trading Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
MACD trading errors can hurt your Forex trading success. One big mistake is relying too much on MACD crossovers. These signals are useful but using them alone can lead to false signals and losses. It’s better to use MACD with other indicators for more accurate predictions.
Another mistake is ignoring the market context. The MACD strategy alone has a win rate of about 62%. But, traders who look at broader market trends and use multi-timeframe analysis can get up to a 68% win rate.
Poor risk management is a big error. Setting the right stop losses is key when using MACD. A strategy with a 1.5:1 reward-to-risk ratio and a 60% win rate after 100+ trades is likely profitable. Remember, MACD crossover strategies need proper risk assessment to work well.
Lastly, many traders don’t adjust MACD settings for their needs. The standard 12-26-9 configuration might not fit all trading styles or timeframes. Trying different parameters can help make your MACD strategy better.
| Common MACD Mistakes | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Overreliance on crossovers | Use additional confirmation tools |
| Ignoring market context | Implement multi-timeframe analysis |
| Poor risk management | Set appropriate stop losses |
| Not customizing settings | Experiment with different parameters |
Optimizing MACD Settings for Forex Trading
MACD optimization is key for successful forex trading. The standard settings (12, 26, 9) are good, but customizing them can make your strategy better. We’ll look at how to adjust MACD settings for different markets and trading styles.
Customizing Parameters
Adjust MACD settings based on market volatility and your trading time frame. For high volatility, try 14 (Fast EMA) and 30 (Slow EMA). In low volatility, use 10 (Fast) and 22 (Slow).
Short-term traders like 6 and 13 days. Long-term traders prefer 19 and 39 days.
Market-Specific Adjustments
Different markets need unique MACD settings. Forex pairs often use 9 (Fast), 19 (Slow), and 7 (Signal). Commodity traders might choose 14, 30, and 9.
Remember, these are starting points. You’ll need to fine-tune based on your strategy and currency pairs.
Performance Testing
Backtesting is key for MACD optimization. Use historical data to see how different settings performed in the past. Then, test them on a demo account to see how they do in real time.
This ensures your MACD settings are optimized for your trading strategy.
Conclusion
The MACD trading system is a strong tool for Forex traders. It uses the MACD line, signal line, and histogram to show market trends. This helps traders spot when trends might change.
It can give both buy and sell signals. This makes it a key part of Forex analysis tools.
Knowing about MACD divergence patterns can help traders. Bullish divergence shows price lows while MACD highs. Bearish divergence shows price highs while MACD lows.
These patterns signal when to buy or sell. The more divergences, the stronger the signal. This helps traders make better choices.
To get the most from MACD, use it with other analysis methods. This makes trading decisions stronger. Remember, using MACD well takes practice and smart risk management.
[ad_2]
لینک منبع : هوشمند نیوز
 آموزش مجازی مدیریت عالی حرفه ای کسب و کار Post DBA آموزش مجازی مدیریت عالی حرفه ای کسب و کار Post DBA+ مدرک معتبر قابل ترجمه رسمی با مهر دادگستری و وزارت امور خارجه |  آموزش مجازی مدیریت عالی و حرفه ای کسب و کار DBA آموزش مجازی مدیریت عالی و حرفه ای کسب و کار DBA+ مدرک معتبر قابل ترجمه رسمی با مهر دادگستری و وزارت امور خارجه |  آموزش مجازی مدیریت کسب و کار MBA آموزش مجازی مدیریت کسب و کار MBA+ مدرک معتبر قابل ترجمه رسمی با مهر دادگستری و وزارت امور خارجه |
 مدیریت حرفه ای کافی شاپ |  حقوقدان خبره |  سرآشپز حرفه ای |
 آموزش مجازی تعمیرات موبایل آموزش مجازی تعمیرات موبایل |  آموزش مجازی ICDL مهارت های رایانه کار درجه یک و دو |  آموزش مجازی کارشناس معاملات املاک_ مشاور املاک آموزش مجازی کارشناس معاملات املاک_ مشاور املاک |
- نظرات ارسال شده توسط شما، پس از تایید توسط مدیران سایت منتشر خواهد شد.
- نظراتی که حاوی تهمت یا افترا باشد منتشر نخواهد شد.
- نظراتی که به غیر از زبان فارسی یا غیر مرتبط با خبر باشد منتشر نخواهد شد.




ارسال نظر شما
مجموع نظرات : 0 در انتظار بررسی : 0 انتشار یافته : 0